What is a Whitepaper in Crypto?
A whitepaper in the crypto industry is a document that covers a blockchain project’s purpose, core idea, and technical framework, often released early to explain how the system works and its long-term vision.
Table of contents:
A whitepaper in the crypto industry is a document that introduces and explains a blockchain project. It defines the project’s main idea, describes its purpose, and presents the technical framework behind it. Typically released at an early stage, the whitepaper describes how the system works, why it was created, and how it plans to function over time.
It serves as a foundational resource for developers, blockchain teams, and digital asset communities who want to understand the technical scope and business logic behind a project.
What Does a Crypto Whitepaper Include?
A typical crypto whitepaper contains several sections that explain how the project operates and what it aims to achieve.
The whitepaper may include:
- Problem. This part explains the specific challenges or inefficiencies the project addresses. It may focus on gaps in scalability, transaction speed, data security, interoperability, or accessibility. A credible whitepaper clearly defines the issue and sets the context for the proposed solution.
- Proposed solution. The document outlines how the project will solve the identified problem. It may involve new blockchain infrastructure, smart contracts, a crypto payment solution, or cross-chain integrations. The explanation often includes examples of business or technical applications to demonstrate practical relevance.
- Technical framework. Here, the whitepaper dives into the architecture of the blockchain network. It usually covers consensus algorithms (like Proof-of-Stake or Proof-of-Work), system components, data structures, and key protocols. Some whitepapers also include details on security layers, smart contract logic, and scalability techniques.
Here’s an example of how technical data is explained in the Ethereum whitepaper:
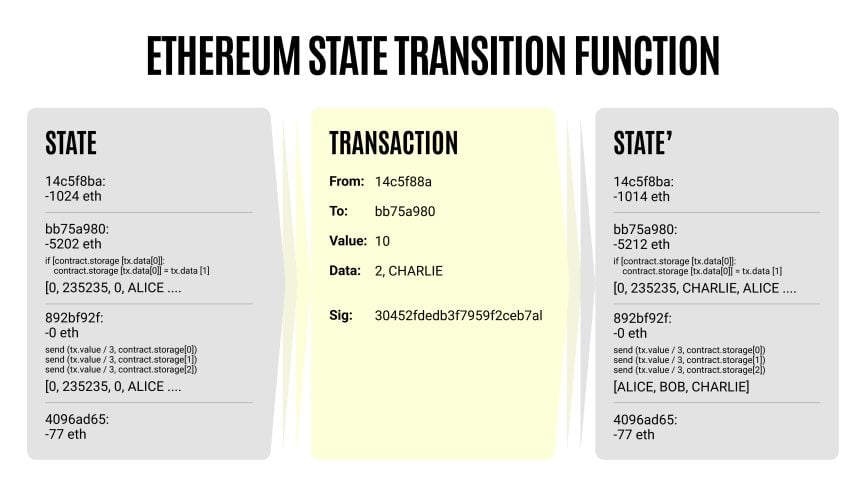
- Token model (tokenomics). This section explains how the native token functions within the ecosystem. It details supply limits, distribution methods, utility cases, rewards for network participation, and potential deflationary mechanisms. Metrics such as vesting schedules, staking rewards, and transaction fees may also be included.
- Roadmap. It shows what has been accomplished and what is planned for future releases. Key stages may include prototype launches, testnets, mainnet deployment, and protocol upgrades.
- Team information. Some whitepapers provide background on the project’s creators, developers, and advisors. This section often highlights past achievements in fields such as blockchain engineering, cryptography, or enterprise software.
The Importance of Whitepapers in Blockchain
Whitepapers act as the first point of contact for developers, platforms, and ecosystem participants. A well-prepared whitepaper gives a detailed view of the project’s goals, architecture, and planned strategy.
These documents help identify whether a use case is realistic and technically sound. Teams working on infrastructure projects often examine whitepapers to determine compatibility, scalability, and integration potential. Communities use them to monitor progress and hold teams accountable to timelines.
Since whitepapers are published openly, they promote equal access to key information, which supports transparency and accountability in the blockchain world.
The First Whitepaper in Crypto
The concept of whitepapers in the digital asset space started with Bitcoin. On October 31, 2008, an individual or group using the name Satoshi Nakamoto released a nine-page document titled Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. This paper introduced a system that enabled peer-to-peer value transfer without intermediaries or centralized control.

The Bitcoin whitepaper outlined essential ideas like decentralized consensus and proof-of-work. These principles became the basis for future blockchain innovations. Since then, releasing a whitepaper has become a standard step for any serious crypto or Web3 project. It acts as a public declaration of purpose, structure, and intent.
Examples of Notable Whitepapers
- Ethereum (2014). Vitalik Buterin’s Ethereum whitepaper introduced a blockchain that supports programmable smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). It expanded blockchain’s role from digital money to a broader platform economy. It proposed Solidity, a new coding language, and Ether (ETH) as the platform’s utility token.
- Zerocash (2014). The Zerocash whitepaper introduced privacy through zero-knowledge proofs (zk-SNARKs). This innovation allowed confidential transactions without disclosing transaction data. Zerocash laid the groundwork for the creation of Zcash, a cryptocurrency focused on user privacy.
- Solana (2017). Anatoly Yakovenko’s Solana whitepaper presented Proof of History, a novel approach to time-stamping blockchain events. It enabled rapid transaction processing and scalability. Solana’s design made it suitable for real-time applications, including gaming, NFTs, and decentralized finance tools.
How Crypto Whitepapers Have Evolved
Since Bitcoin’s whitepaper set the standard in 2008, the format and focus of crypto whitepapers have changed significantly. Ethereum’s introduction of smart contracts in 2013 marked a shift toward programmable blockchains and more complex ecosystems.
By 2017, during the initial coin offering (ICO) boom, whitepapers became common tools for explaining both technical foundations and token models.
However, this period also exposed weaknesses in the format — some projects published vague or misleading content, which led to skepticism.
Today, whitepapers are more structured and transparent. Teams are expected to provide technical depth, real-world application scenarios, and measurable roadmaps.
Conclusion
A whitepaper in crypto is a foundational document that outlines a blockchain project’s vision, technical framework, tokenomics, and roadmap. It’s typically released in the early stages to communicate a project’s value proposition, technical design, and governance to developers, investors, and the broader community. Much like a business plan for startups, a whitepaper builds trust, transparency, and credibility—crucial in the decentralized space.
For anyone considering supporting or investing in a crypto project, reading the whitepaper is essential to understand its long-term viability and technical integrity.
Other Terms from the Crypto Industry